Differentiate yourself from being a mimicker of training methods by becoming a true technologist of dog obedience instruction.
Objectives
- Trust Bloom's Taxonomy to become an expert
- Understand universal scientific dog training terminology
- Analyze and evaluate dog training instruction
- Create clean and scalable dog training instruction
Trust Bloom's Taxonomy
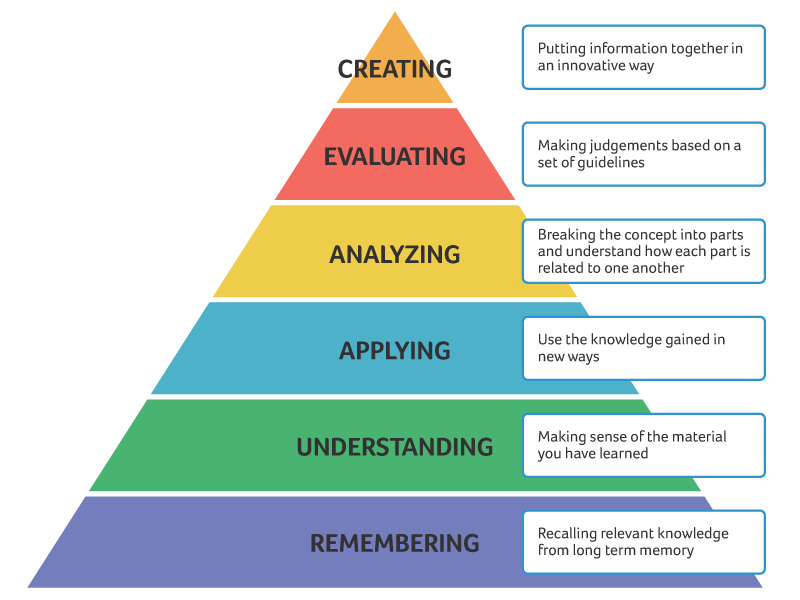
Overall Purpose
Bloom's Taxonomy is a framework developed by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues in 1956 to classify educational goals and objectives into a hierarchy.
Breakdown of the Purpose of Each Step
Bloom's Taxonomy is traditionally divided into six levels, arranged in a hierarchy from lower-order to higher-order thinking skills. Each level has a specific purpose in the educational process.
1. Remembering:
- Purpose: To recall basic facts, concepts, and information.
- Example Activities: Memorizing the quadrants of operant conditioning and their meaning, schedules of reinforcement, etc...
2. Understanding:
- Purpose: To grasp the meaning of information and interpret it.
- Example Activities:
- Summarize the concepts of operant conditioning in your own words to a client.
- Explain why removing attention from a dog is negative punishment.
3. Applying:
- Purpose: To use information in new situations or contexts. Apply knowledge, facts, techniques, and rules in a practical way. It involves executing and implementing.
- Example Activities:
- Design clean instruction that reflects what is expected in theory.
- Limit trial and error by KNOWING before DOING.
4. Analyzing:
- Purpose: To break down information into its component parts and examine relationships.
- Example Activities:
- Watching training sessions and determining what behaviors from the dog were created by certain parts of the training plan.
- Analyze how different techniques may serve the same purpose.
- Determine if a desired step may be missing from the training plan.
- Break down another training company's methods with minimal observation.
- Recognize side effects in a training plan and what may have caused them.
- Fill out an accurate obedience checklist for a dog you have not trained simply by observing a training session.
5. Evaluating:
- Purpose: To make judgments based on criteria and standards.
- Example Activities:
- Determining if the instruction is fair and humane.
- Determining if the instruction is effective for the task.
- Determining if the instruction if the instruction is clean.
What is clean instruction?
When someone says that "the instruction is clean" in the context of evaluating instructions, they typically mean that the instructions are clear, concise, and easy to understand. "Clean" instructions usually have the following characteristics:
- Clarity: The instructions are straightforward and leave little room for misunderstanding.
- Conciseness: They avoid unnecessary words or overly complex language, getting to the point efficiently.
- Organization: The steps are logically ordered and easy to follow.
- Precision: Each step is specific, providing just enough detail without being wordy.
- Readability: The language is simple, and the instructions are often formatted in a way that is easy to read (e.g., using bullet points, numbered lists, or headings).
6. Creating:
- Purpose: To produce new or original work by integrating knowledge. This is the highest level, involving generating, planning, and producing. Learners use their knowledge and skills to create something new and innovative.
- Example Activities:
- Designing a new training tool to solve a unique problem.
- create training instruction for a scalable business.
- create training instruction to reflect the unique needs of an unusual request.
- create a training or dog handling curriculum for a working dog program.
Important concepts to master in the course
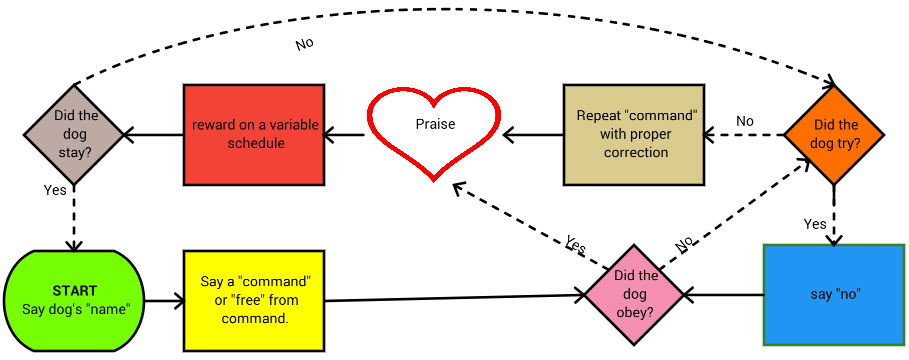
Command Structure Building and Analysis
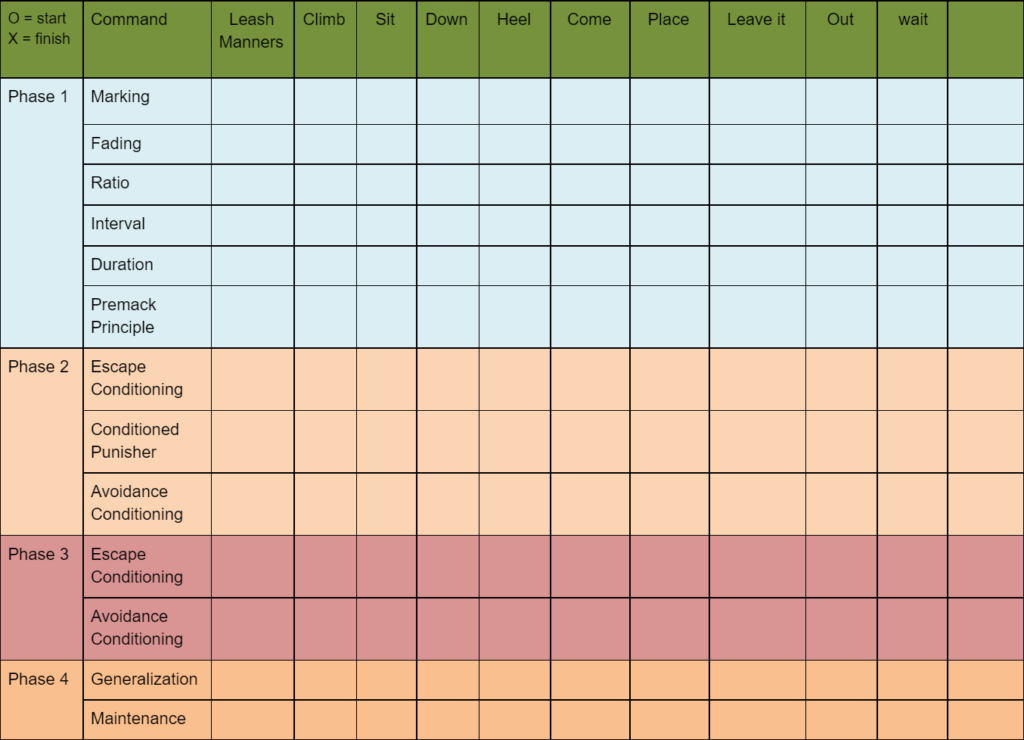
Understanding and Applying a Checklist
Creating Instruction!
Summary
By progressing through the levels from basic knowledge recall to creative application, students develop deeper understanding and higher-order thinking skills, ultimately preparing them for complex problem-solving and critical thinking as dog training professionals.


Responses