Objectives
- What is attitude from a social psychology perspective?
- Why is it important for professional dog trainers to understand?
- What are things to consider when atempting to create or alter an attitude?
What is Attitude?
A settled way of thinking or feeling that typically is reflected in a person's behavior.
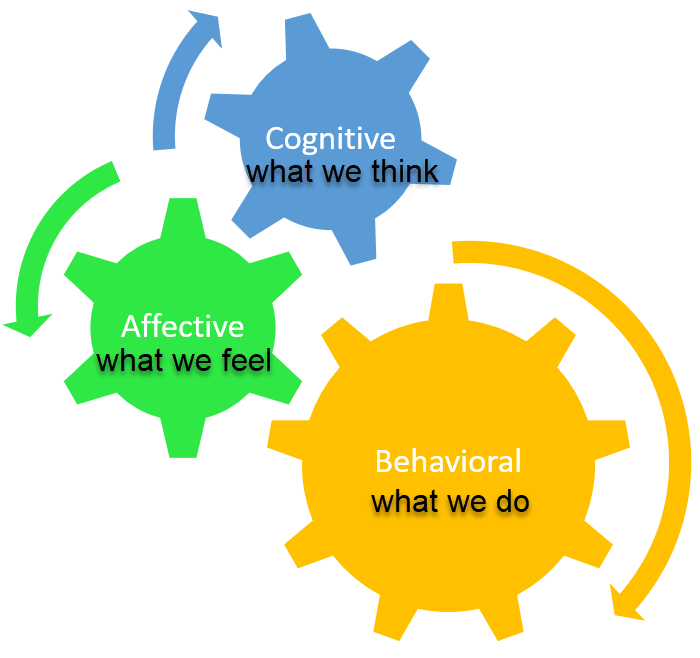
It consists of three components. They all relate to each other:
- Affective - what we feel
- Cognitive - what we know through experience
- Behavioral - what we do
Examples:
I think pit bulls are so cute. I read that were used as nanny dogs. They make me feel warm and fuzzy inside when I see them. I will adopt one and snuggle on the couch with it.
I know someone who was injured by a pit bull. When I see a pit bull I get scared. I signed a petition to have them banned in our city.
I volunteer at the local shelter and walk a pit bull. He is always happy to see me and very affectionate. I get angry when people say they are dangerous dogs.
I am studying to be a dog trainer and research all dog breeds before I train them. I have learned that all dog breeds have certain tendencies and that every dog also has individual temperaments. I admire the athleticism of pit bulls and feel that they can be great dogs with knowledgeable and responsible ownere.
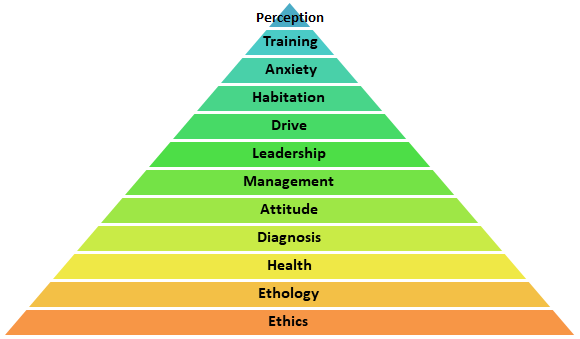
Why is attitude above diagnosis in Foundation Style Dog Training?
The breakdown of a successful attitude can find sources in a poor foundation of:
Ethics - LIMA, CYNOPRAXIS
ETHOLOGY
Diagnosis
Examples:
Creation of incompatible attitudes:
- Villifying a dog is a jerk, dick, etc..
- Making a dog an unemotional creature: dog is self serving, does not "love" you.
- Overly simplifying a dog's capabilities: punishment is abusive to dogs
Leads to incompatible behavior from clients:
- poor management
- poor leadership
- poor consideration of basic needs
- Poor behavior plans
- Lack of implementing LIMA
- Loss of overall potential results and a cynppraxic outcome
We need our clients to be:
- dedicated - often longer than they initially realized
- Not have bias about training tools and techniques that do not refect scientific law
Common Ways Attitude Leads to Behavior
Event - memorable (dog injured by a trainer) Dog got hit by a car after working with trainer.
Norms - How will you be perceived by others?
Perception of control over behavior - Is it possible? Do I have time to do otherwise?
Past behavior
Modeling
Intentions - Public perception? Privately solve a problem with their own dog? Etc..
Behavior can also influence attitude.
Foot in the door - agree to small things and to bigger things until they believe
Role-playing - follow the part, be liked. then the new behavior becomes the attitude we have.
Cognitive Dissonance
The discomfort we have when components of attitude contradict. Therefore we adjust. The tendency of Confirmation Bias
Confirmation Bias
The tendency to only seek out and remember information that aligns with their pre-existing views and ideas.
How do we change attitude?
Understand the elaboration likelihood model
3 stages:
Target characteristics?
the target - are they tired, angry, not capable of understanding the vocabulary.. Is it important to the person, is there a reason to be motivated? More motivated people pay attention to the content.
Quality of the message/presentation?
The target audience will either be influenced by the central or peripheral route (the information itself or the presentation itself)
Central -the quality of the information.
Peripheral - How well or attractive the presentation - superficial. - seeing
Less motivated people pay attention the attractiveness of the presentation, impressive power point, etc.. Was it fun. Did the presenter get the audience to laugh, etc..
Likelihood of attitude change?
Highly motivated people get a deeper understanding and created attitudes are more permanent.
Less motivated people who are influenced by the peripheral route are more likely to have temporary attitude changes.


Responses