Objectives
- What is Balancing the Drive?
- What are Motivating Operations?
- Establishing Operations
- Abolishing Operations
- What are prerequisites to consider?
- What are some examples of how a trainer may balance the drive for specific reasons?
What is "Balancing the Drives?"
Animal Drive - Biological forces that stimulate the (individual) animal toward certain (all?) behavior.
- Eating
- Chasing
- Playing
- Social interaction
- Etc..
Balancing the Drive - Practices used to increase or decrease the intensity of those drives.
Increasing the drive toward a behavior can help overcome competing drives (mating, avoidance of cold/heat/discomfort, etc..)
Study to reference: Study of Animal Drives, Fred A. Moss 1924
Understand Motivating Operations
Motivating operations (MO) are environmental variables that:
- alter the effectiveness of a reinforcer, and
- alter the current frequency of all behavior that has been reinforced by that reinforcer
MO can also be categorized into one of two defining effects:
- Establishing Operation (EO) - increases the current effectiveness of reinforcement
- Abolishing Operation (AO) - decrease the current effectiveness of reinforcement
Examples:
- Dog trains longer for treats if it is hungry (EO), or may not offer any behaviors for treats if it is full (AO)
- Similar examples utilizing affection and play as reinforcers
Prerequisites
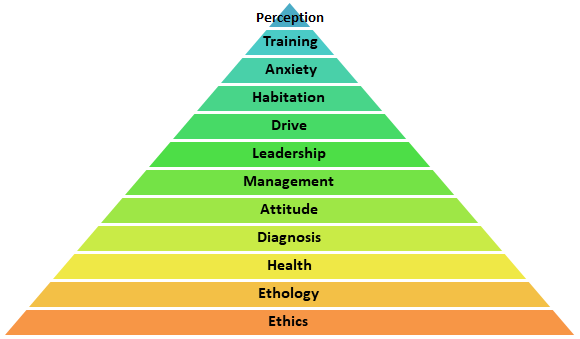
Ethics - Cynopraxis, ABA
Ethology - Understand the function of the behavior to find best alternatives.
Health - Is it a health problem?
Diagnosis - Is the client correct? What symptoms are you getting. Address all possible causes.
- chewing, chasing, barking, etc..
Attitude -
- "If they are a jerk without exercise they will just be a fit a jerk with exercise"
- Balancing the drive is more than physical activity, it is also satisfying psychological drives.
Management -
- Choose carefully how to manage a dog
- Too much confinement can cause deficits in multiple areas (food, social, physical, play, etc..)
- Know your history and the reason for modern dogs spending extended periods in small kennels.
- Intense drives on competition fields
- Low rate of mentally balanced and housebroken dogs
Leadership -
- Sets the stage for balancing the drives by putting the owner/trainer in control of the important variables needed for training and making behavior changes.
Understanding the foundation and the importance of balancing the drives for each individual situation is critical for effective housebreaking plans and training behaviors.
Examples of how balancing the drives are important for SPECIFIC training situations:
Explosive Detection Dog:
- Play drive left in deficit
- Food drive kept satiated
Family Puppy
- Play drive satiated
- Food drive in deficit (certain times of the day)
Understand the roots of behavior problems and satiate the drive on a reasonable schedule.
For most pets we are finding ways to satisfy/satiate:
- Chewing furniture (give bones)
- Biting and pulling curtains/clothing/etc (play tug)
- Chasing (play fetch)
- Obtrusive social behavior (plan training sessions and situations where the dog recieves affection)
For most working dogs and to a lesser degree pets we may need to cause deficits in the satisfaction:
- Detection dogs
- Sport dogs
- etc..
Every Plan is Usually Unique


Responses